The prerequisite condition concept is one of the key concepts of Control-M production control.
Prerequisite conditions enable the establishment of job dependencies and, when a job normally requires manual intervention, such as determination that a cartridge arrived on-site, ensures that the manual conditions are satisfied before the job is submitted.
A prerequisite condition is a user-defined, descriptive name given to a certain situation or condition. Prerequisite conditions can be specified in any of three types of statements in a job scheduling definition:
Table 14 Prerequisite Condition Statements
Statement |
Description |
|---|---|
IN statements |
These statements must be satisfied (that is, the prerequisite condition must exist) before the job can be submitted. |
OUT statements |
These statements are performed, that is, the prerequisite conditions are added or deleted, only when the job ends OK. |
DO COND statements |
Whether these statements are performed (that is, the prerequisite conditions are added or deleted) depends on the execution results of the job. DO statements in a job scheduling definition accompany ON statements. The ON statements define step and code criteria. If the specified code criteria are satisfied for the specified steps, the accompanying DO statements are performed. |
In its most basic form, a prerequisite condition is defined in an IN statement in one job, and as an OUT (or DO COND) statement in another job. This makes the execution of the one job dependent on the execution of the other job.
Prerequisite Condition Example
Figure 1 Establishing Job Dependency by Prerequisite Conditions
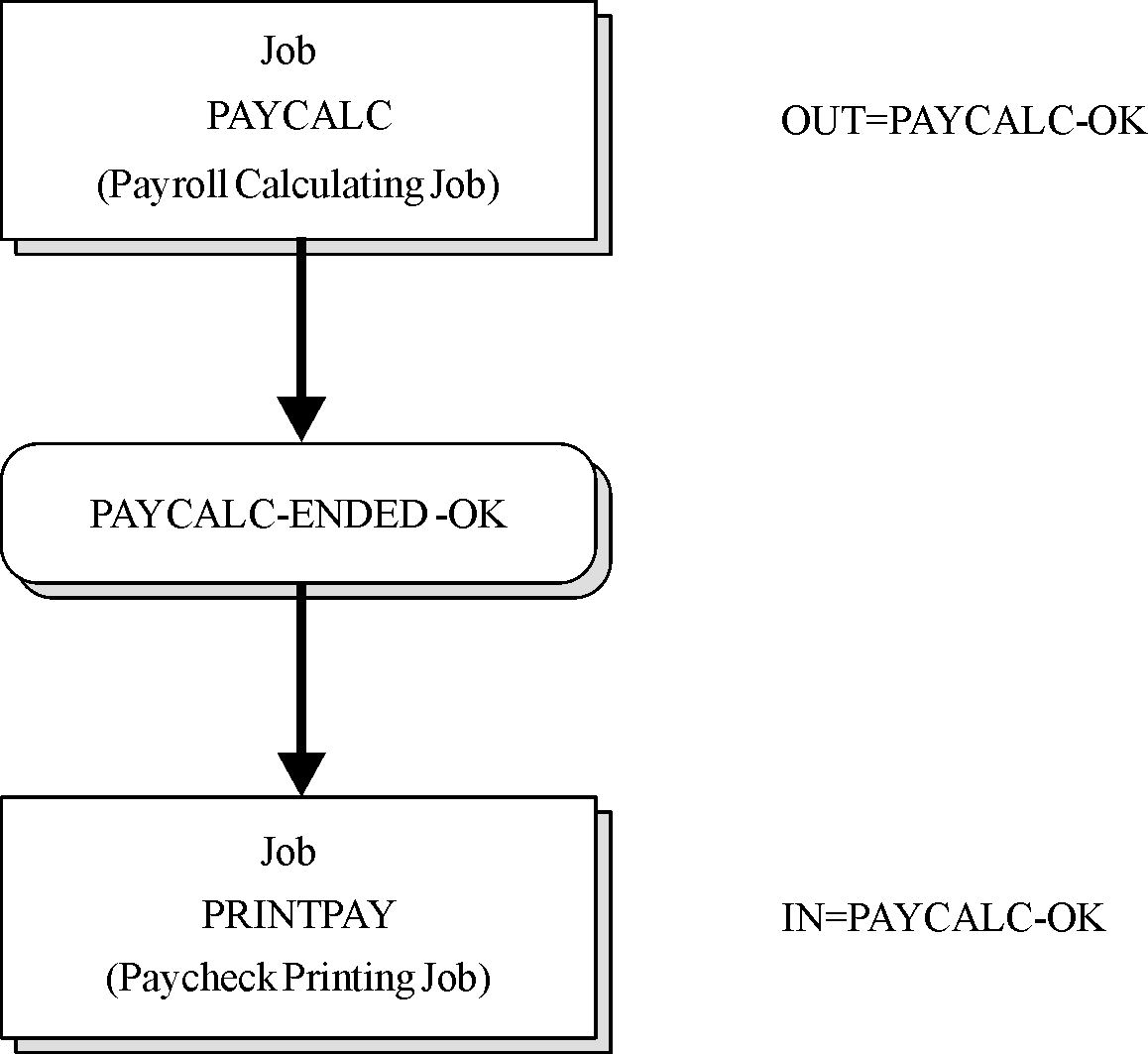
Payroll-calculating job PAYCALC must be run before Payroll-check-printing job PRINTPAY. To create the necessary job dependency, a prerequisite condition is defined as follows:
Because the condition required by job PRINTPAY is not created unless job PAYCALC terminates successfully, the dependency of job PRINTPAY on job PAYCALC is established.
Job dependencies do not have to be as simple as the above example illustrates. An almost unlimited number of conditions and job dependencies can be created:
In SMART Tables (described in Handling of Jobs), prerequisite conditions can be defined as the following SMART Table parameters: IN, OUT and/or DO COND statements. In this case, they apply to the entire set of scheduled jobs.
Parent Topic |