This chapter describes the CA-TLMS to Control-M/Tape conversion process. A brief description of the differences between CA-TLMS and Control-M/Tape is followed by detailed conversion steps.
Conversion to Control-M/Tape is currently supported for CA-TLMS versions 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 12.6, and 14.0. CA-TLMS is comprised of the following primary components:
Table 8 CA-TLMS Primary Components
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
Volume Master File (VMF) |
Volume and dataset information for each volume in the tape library. |
Retention Master File (RMF) |
User-defined policies for storage (i.e., vaulting) and retention management. |
Tape Retention System (TRS) |
Performs retention and storage procedures according to information in the VMF and RMF. |
Online Recorder |
Accesses and maintains the VMF according to tape activity at the site. |
CA-TLMS Scratch Pool management can be used to restrict certain datasets to specific tape volumes.
Control-M/Tape volume and dataset information is stored in the Control-M/Tape Media Database (MDB). When a dataset is created, Control-M/Tape records dataset attributes in the relevant dataset record in the Media Database and updates the appropriate volume record. Dataset access is tracked in both records. As Control-M/Tape rules are processed, changes to media management attributes (e.g., vault patterns and retention periods) are updated in the Media Database.
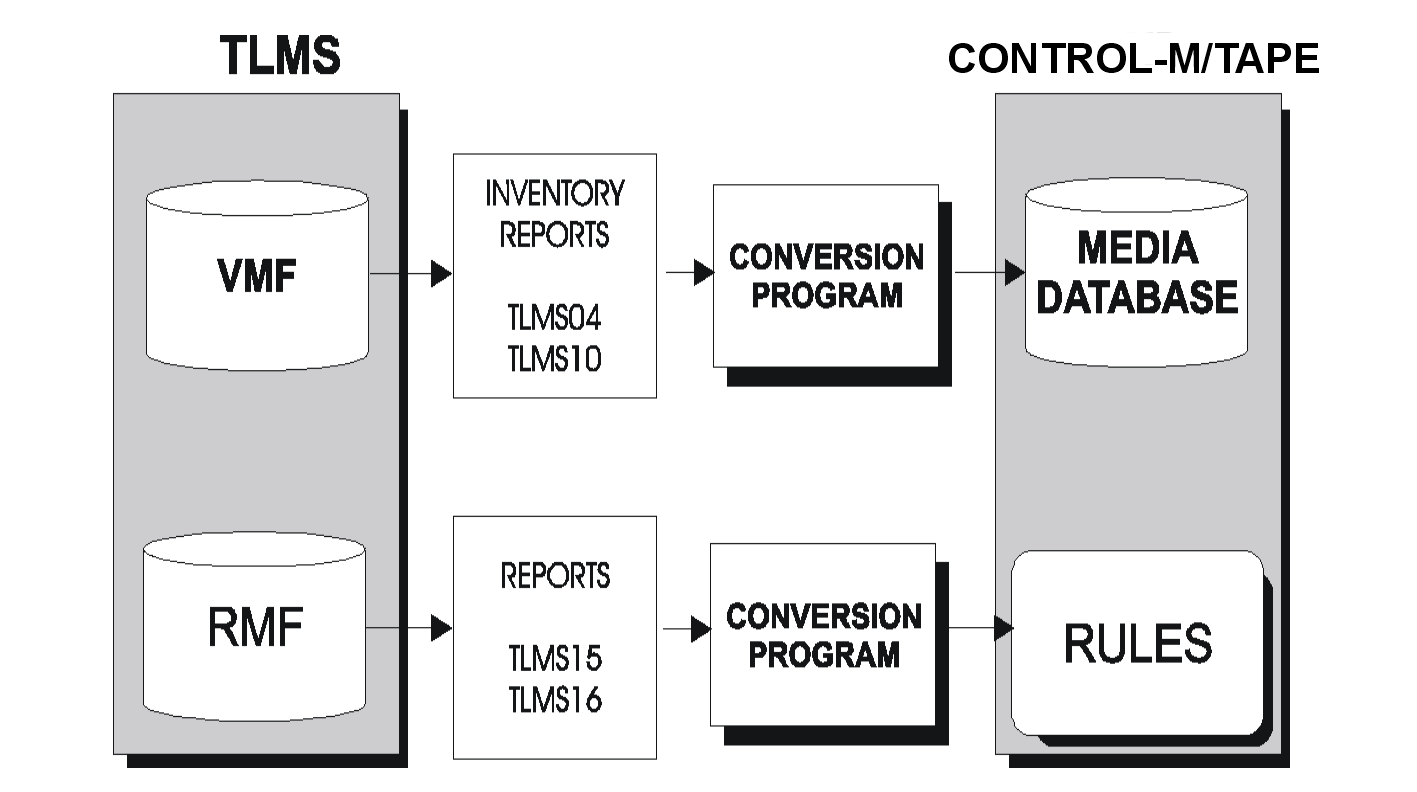
The following diagram indicates how the major CA-TLMS components are converted to Control-M/Tape format.
Figure 7 Conversion of CA-TLMS Components to Control-M/Tape
Parent Topic |