Assigns a value to a Control-M/Analyzer Database, AutoEdit, or Local variable. The value assigned to the variable is extracted from the dataset being processed by the current EXECUTE block.
Figure 196 DO EXTRACT Statement Format
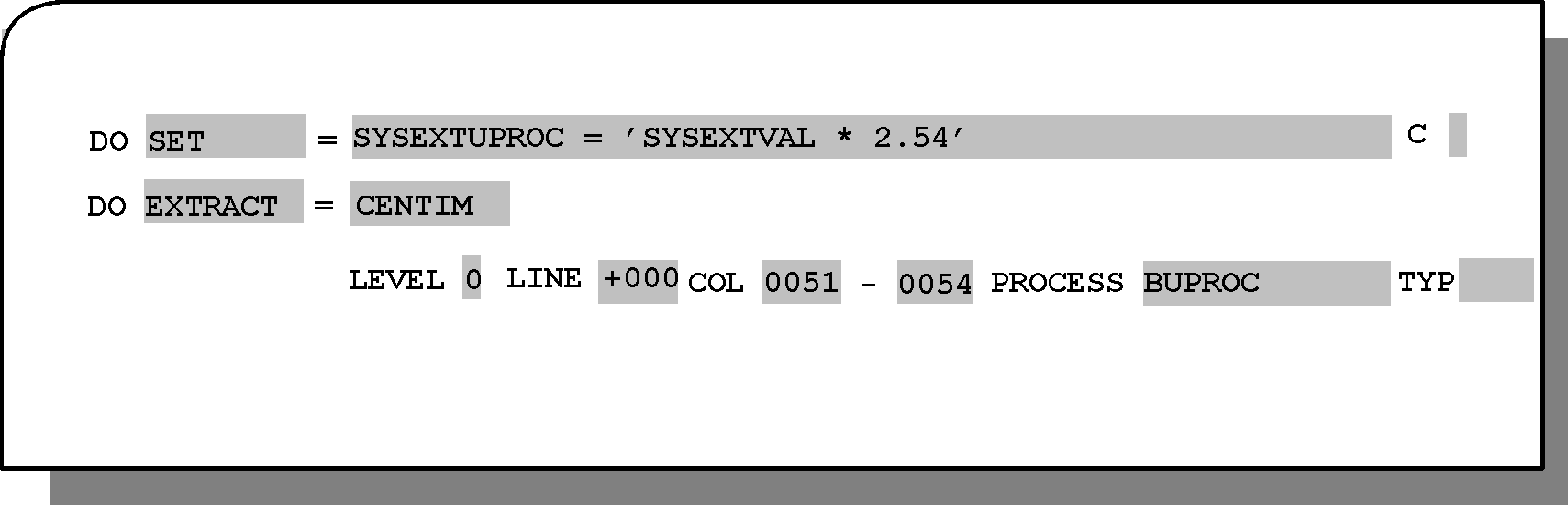
Optional. The DO EXTRACT statement is not available in an EXECUTE block containing an ON DATA statement.
Type the word EXTRACT (or its abbreviation EXT) to the right of the DO parameter label on the Rule Definition screen. Press Enter and the = prompt with the following fields is displayed:
Table 225 DO EXTRACT Statement Fields
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
varname |
Name of the AutoEdit, Database, or Local variable in which the extracted information is to be stored. Mandatory. |
LEVEL |
Level of the WHEN statement in the current WHEN criteria that is to be used as a reference for this extraction. The default is the current level (which can be specified as level 0). See statement WHEN for additional information. Optional. |
LINE |
Specifies how many lines Control-M/Analyzer should skip when positioning within the data source before extracting. A signed (+/-) 3-digit number must be specified. Mandatory. Valid values are specified and described in Table 226. |
COL |
Specifies the column range from which to extract data, comprised of:
Valid values are specified and described in Table 226. Notes: Line and column positions can also be specified using Relative Values (for example, the column at which the WHEN string was found plus an offset value). For more information, see General Information. The number of columns in the COL range cannot exceed 100 because the maximum length of the variable value (after resolving %% operators, if any) is 100 bytes. |
PROCESS
|
Type of processing to apply to the extracted value before setting the variable. Optional. Built-in processes all begin with the letter B. The following built-in processes are available:
For more information about most of these processes, see DO EXTRACT Processes. User-defined processes must begin with the letter U. User Exit CTBX010 can be modified to call user-defined processes. For information about User Exit CTBX010, see the IOA.SAMPEXIT library. For information about compiling and linking member CTBX010, see the INCONTROL for z/OS Installation Guide. |
TYP |
Type of extraction to perform when setting the variable. Optional. Valid values are:
|
Parent Topic |