This section describes how to establish parallel sessions between the following specific client applications:
Note: SNA Server can also be configured to support single-session logical unit (LU) dependent connections to IOAGATE.
Enabling parallel sessions between the client applications and IOAGATE allows sessions to connect to their respective repositories through a single logical unit.
Note:The steps for mainframe-related configuration activities are provided in the following topic. For non-mainframe related steps, see the documentation of the relevant client application.
To support parallel sessions, the following components must be configured:
Note:References to Microsoft SNA Server in the following section include Microsoft Host Integration Server 2000 and 2004.
Changes must be made in VTAM and IOAGATE to support parallel sessions.
To enable parallel session support:
Note:The SNA server physical unit (PU) connection must support PU 2.1.
To verify the XID type used by the SNA connection:
Open Microsoft SNA Server Manager.
Note: SWPU30 is used as an example connection name.
The Connection Properties dialog box is displayed.
Figure 50 Connection properties – General tab
Figure 51 Connection properties - System Identification tab
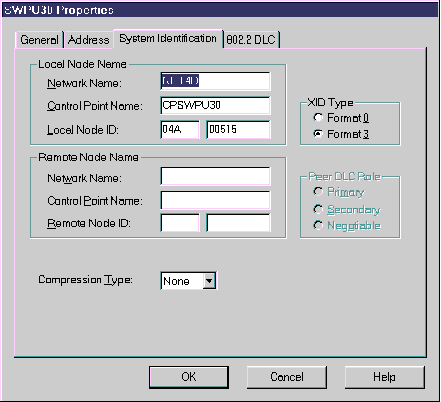
In the XID Type field, select Format 3 and click OK.
For more information on defining a PU that supports an independent logical unit, see the Microsoft SNA Server Administration Guide.
Example
SWPU30 PU ADDR=01,
CPNAME=CPSWPU30,
PUTYPE=2,
XID=YES,
...
LUPRL LU LOCADDR=0
VBUILD TYPE=APPL
PODLUP APPL AUTH=(VPACE),
DSESLIM=256,/* Max concurrent logged on users */
OPERCNOS=ALLOW,
APPC=YES,
VPACING=7
Note: Do not specify DLOGMODE or MODETAB.
The logical unit (LU) name PODLUP can be changed if you alter all references to it.
Note: When a new logical unit is defined, the DSESLIM takes effect immediately. When adding DSESLIM to an existing LU (and performing INACT and ACT), DSESLIM does not take effect immediately.
The following CNOS command can be used to set the parallel session limits to take effect immediately:
F VTAM,CNOS,ID=PODLUP,LUNAME=LUPRL,LOGMODE=#INTER,LIMITS=(256,0,256)
where PODLUP is the name of the remote LU and LUPRL is the name of the local LU.
Parent Topic |