Each chapter in this guide contains a table that lists all the protected elements applicable to the INCONTROL product for that security is implemented. It is recommended that the security administrator review the table to determine the user categories and authorizations required for the protected elements in the INCONTROL products. Members (IOASRAC3 and CTxSRAC3, IOASTSS3 and CTxSTSS3, and IOASSAF3 and CTxSSAF3) in the IOA INSTWORK library contain examples that can be used as a basis for specifying the required authorizations. The job is created in the IOA INSTWORK library after selecting the "Functions Security Definitions" step in ICE.
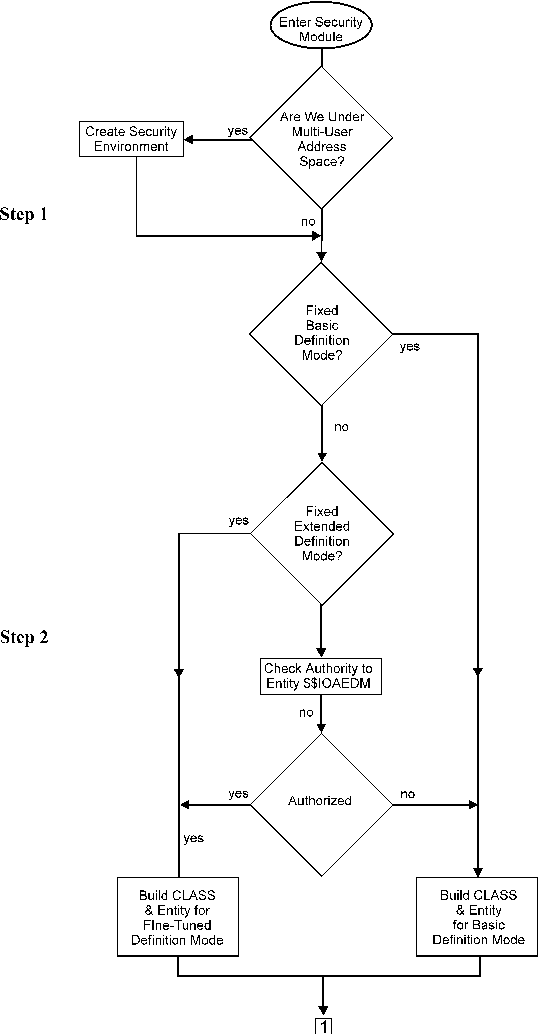
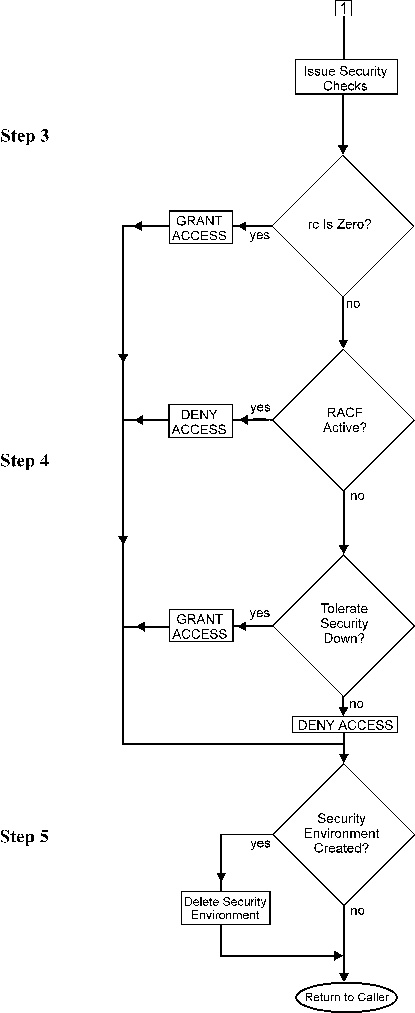
The steps below describe the flow of the IOA security implementation process.
IOA security interface modules verify that a specific user is authorized to perform a specific action. If the protected components belong to a multiuser address space (such as the Control‑M monitor, the Control‑D monitor, or the Online monitor) it is necessary to determine the security profile of the user within the address space. When an IOA security module is invoked under a multiuser address, the IOASECUR module determines the security profile. This service identifies the user requesting the action and builds the user’s security profile in storage. Otherwise, the user maintains the same security profile as that of the address space.
Once the security environment is determined for the user ID, the security interface determines which definition mode is required for the specified user ID or security module. The appropriate entity and CLASS are built for the user ID.
If the chosen mode is conditional, a check for the Extended entity ($$xxxEDM) is performed and the appropriate entity and CLASS are built based on the check results. If the chosen mode is Fixed Definition mode, the appropriate entity and CLASS are built.
The IOASECUR IOA security services module is invoked to perform the authority check.
If the user is authorized to the specified entity, an application return code zero (authorized) is returned. If the return code from the security product indicates that the security product is not active or the specific entity is not defined to the security product, the security interface module either grants or denies the request, according to the SECTOLx security installation parameter.
Once the authorization process is complete, the security environment is cleaned up.
The following diagrams illustrate the detailed flow of the INCONTROL security modules, representing each of the steps described above.
Parent Topic |